If you’re deciding between AMD Radeon 890M vs 780M, it depends on your needs. Here’s what you need to know:
- Radeon 780M: ideal for students, office work, light gaming and ultra-portable mini PCs. More energy-efficient, it offers good fluidity on eSports games and standard multimedia tasks.
- Radeon 890M: designed for demanding gamers, content creators and professionals who use local AI. It has more compute units, a higher GPU frequency and an integrated NPU. This allows it to deliver superior performance in gaming, video editing and creative applications.
In summary, for everyday and economical use, the Radeon 780M is more than sufficient. If you want to fully exploit the capabilities of a high-end mini PC or Ryzen AI laptop, opt for the 890M.
Introduction: Two Powerful iGPUs for 2025
In 2025, Ryzen processors confirm the rise in power of iGPUs (integrated GPUs). Particularly with two flagship references: the Radeon 780M and the Radeon 890M. These integrated GPUs are no longer simply backup solutions. They now allow you to game, create and work efficiently on ultra-compact machines. Particularly on mini PCs and ultraportables.
The Radeon 780M, based on the RDNA 3 architecture, equips Ryzen 7040 processors (e.g. Ryzen 7 7840U, Ryzen 9 7940HS). It offers an excellent balance between performance and energy efficiency.
The Radeon 890M, meanwhile, introduces RDNA 3.5 and an integrated NPU, intended for local artificial intelligence tasks. This is a real asset for image processing, blurring or real-time effect generation. It can be found among others in the Ryzen AI 9 HX370 and Ryzen 7 HX365 processors.
These iGPUs play a central role in the evolution of new generation mini PCs. And for good reason, power, battery life and compactness have become inseparable. Recent models like the GEEKOM A8 (Radeon 780M) and GEEKOM A9 Max (Radeon 890M) embody this trend.
Whilst these two graphics cards have similarities, certain elements distinguish them. It’s essential to compare them in order to find the model that corresponds to your usage.
👉Also read: AMD Radeon 890M: Complete Performance Guide
Technical Specifications Compared
Let’s get straight to the point with a comparison table of the AMD Radeon 890M vs Radeon 780M:
| Characteristics | AMD Radeon 780M | AMD Radeon 890M |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | RDNA 3 | RDNA 3.5 |
| Compute Units (CU) | 12 | 16 |
| GPU Frequency | ~2700 MHz | ~2900 MHz |
| Shared Memory | LPDDR5 / LPDDR5X | LPDDR5X / LPDDR5T |
| AI/NPU Support | No | Yes (Ryzen AI 9 HX370, etc.) |
| Compatibility | Ryzen 7 7840U, Ryzen 9 7940HS | Ryzen AI 9 HX370, Ryzen 7 HX365, etc. |
The Radeon 780M, based on the RDNA 3 architecture, marks a clear evolution compared to previous Vega iGPUs. Particularly thanks to its 12 compute units and its high frequencies which can reach 3 GHz (depending on the processor). It’s integrated into Ryzen 7040 Series processors, which are very common in high-performance mini PCs and ultraportables.
For its part, the Radeon 890M adopts the RDNA 3.5 architecture. A change that offers more compute units (16 CU) and better frequencies (up to 2.9 GHz). It also introduces hardware AI support thanks to a dedicated NPU. The latter is directly integrated into the new Ryzen AI 300 Series processors. This combination enables significant gains in graphics performance. But also in local AI tasks such as upscaling or visual effects generation.
But these aren’t the only improvements. Memory compatibility also evolves. The 890M exploits LPDDR5T, which is faster. This improves graphics bandwidth and system responsiveness. It’s a real asset for machines oriented towards gaming and creation.
Gaming Performance: The 890M Takes the Lead
With the arrival of the Radeon 890M, AMD takes a new step in the iGPU sector. Thanks to its RDNA 3.5 architecture and its 16 compute units, it offers a net performance gain. Particularly compared to the Radeon 780M under RDNA 3. The first independent tests show notable differences. Particularly in recent 3D games. And this, whilst maintaining excellent energy efficiency.
Concrete Results in 1080p
According to published benchmarks, the Radeon 890M delivers between 20% and 30% additional FPS on average. And this, on the majority of AAA games in 1080p. On Cyberpunk 2077 or Shadow of the Tomb Raider, for example, it reaches around 55–60 fps on “medium”. The Radeon 780M runs at around 40–45 fps.
This progression is explained by the increase in the number of Compute Units (+33%). But also by the presence of better memory bandwidth thanks to LPDDR5T.
But this difference is even more noticeable on eSports games. In Valorant, CS2 or Fortnite, the 890M easily maintains more than 120 fps in 1080p, even with medium settings. This ensures perfect fluidity on 120 Hz screens. The 780M, meanwhile, remains very playable (80–100 fps) but reaches its limits more quickly in demanding scenes.
Regarding consumption and thermals, the advantage also goes to the Radeon 890M. Even though it displays a higher TDP (45 W), it’s better controlled. The RDNA 3.5 architecture improves the performance/watt ratio by nearly 32%.
For What Type of Gamer?
Depending on your gamer profile, one of the two models will suit you best. Here’s what you need to know to make the right choice.
The Radeon 780M remains an excellent choice for casual gaming or undemanding titles. Such as indie games, MOBAs, eSports, or older AAA titles. Coupled with a Ryzen 7 7840U or a mini PC like the GEEKOM A8, it allows you to game comfortably. And this, without neglecting energy efficiency. This is an important advantage for mobile users.
For its part, the Radeon 890M clearly targets the demanding gamer and content creator. It equips more powerful processors like the Ryzen AI 9 HX370. Which is itself integrated into high-performance mini PCs such as the GEEKOM A8 MAX or A9 MAX. The 1080p performance approaches that of a GeForce GTX 1650 Max-Q. But whilst maintaining the advantages of an iGPU. That is, silence, low consumption and the absence of a dedicated card.
In summary, if you’re a casual gamer, the Radeon 780M remains ideal. However, if you’re looking for the best integrated gaming experience in 2025, the Radeon 890M is the one you need.
Content Creation and Productivity
The latest generation iGPUs no longer simply manage the desktop and games. They also support demanding creative workflows. Particularly thanks to the integration of hardware acceleration functions and AI pipelines. The difference between the AMD Radeon 890M vs 780M is particularly revealed in this area. And this, both in terms of encoding and video editing as well as stability during extended multitasking.
Encoding, Editing and AI
As we mentioned, the Radeon 890M is embedded in the AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 generation processors. They integrate an NPU (Neural Processing Unit) dedicated to AI processing. Such as local upscaling, intelligent blurring or image generation. According to the specifications, the APU displays an XDNA 2 NPU capable of operating up to 50 TOPS.
This integration allows workflow simplicity to improve. For example, in software like DaVinci Resolve, Adobe Premiere Pro or Blender, the 890M can accelerate 4K or 1080p export. It can also take advantage of hardware encoding and relieve the CPU on AI effects.
In contrast, the Radeon 780M, although effective for 1080p editing and photo retouching, doesn’t integrate an NPU. It remains more limited for local AI tasks or rapid exports. Tests show that the 780M can suffice for “amateur creation” use. However, it cannot rival the fluidity of a “pro” AI-assisted workflow.
Multitasking and Energy Efficiency
For multitasking (editing, export, rendering, visual effects), memory management, TDP and thermal dissipation are essential. The 890M shows better stability under prolonged load and more controlled energy behaviour than the 780M. Particularly thanks to its optimised RDNA 3.5 architecture and its support for LPDDR5X/LPDDR5T memory (via the Ryzen AI APU).
In comparison, the 780M must often work with U-series configurations with limited TDP. Which can lead to frequency drops during video export or long renders.
Concretely, for a creator who regularly exports projects and wants a more durable and fluid machine, the 890M is recommended. For occasional and light use, the 780M remains an effective and economically interesting option.
Office Work, Multimedia and Daily Use
If we set aside heavy gaming or creative uses, the AMD Radeon 780M and AMD Radeon 890M show that they’ve evolved. Both offer excellent fluidity in general use. Such as web browsing, office work, 4K streaming or light editing. User feedback and tests on Windows 11 or Linux platforms show that these chips can handle daily tasks. And this, without the slightest hitch.
Nevertheless, there are a few differences. But they remain minimal. For browsing, video streaming or document editing, the 780M is largely sufficient. It proves very high-performing, as we found during our tests. Moreover, it’s integrated into thin and light computers.
However, the 890M brings additional room for manoeuvre. But it’s not necessarily noticeable for “pure” office use.
On the other hand, if you use ultraportable machines, or if you’re sensitive to battery life, the Radeon 780M is recommended. It’s less power-hungry and well integrated into thin formats. It allows you to combine acceptable performance and low consumption. If your use focuses on emails, the web, videos and some light photo editing, opt for the 780M. It’s a logical and effective choice.
Compatibility and Ecosystem
Whether for Radeon 780M or 890M, software support relies on the AMD Software suite. Particularly Adrenalin Edition. AMD regularly publishes versions compatible with its APUs and integrated GPUs. This is the case for example with version 25.10.2 intended for Ryzen AI processors (including the 890M). And which has been available since October 2025.
From a hardware point of view, the Radeon 780M equips machines offering modern interfaces, such as HDMI 2.1 or DisplayPort 2.1. But also USB4 support, which allows it to be connected to 4K or multiple screens. Without having to adapt external solutions.
The 890M, meanwhile, is expected in “Ryzen AI” platforms. These have the same connectivity standards (USB-C/USB4, potentially Thunderbolt depending on the integrator).
For compatibility with external graphics enclosures (eGPU) or USB4/Thunderbolt docks, the USB4 port allows advanced configurations. Of course, actual use depends on the system and manufacturer.
In summary, software is well supported via Adrenalin Edition for both GPUs. Hardware, ports and connectivity, is already aligned with 2025 standards. However, it should be emphasised that the 890M offers a bit more elasticity for high-end platforms.
Which Radeon to Choose According to Your Profile?
To choose between AMD Radeon 890M vs 780M, you must analyse your main usage. Both options are high-performing but they have different strengths. The 780M prioritises energy efficiency and fluidity for standard tasks or light gaming. The 890M stands out for its increased performance, its integrated NPU and its better stability under prolonged load.
Here’s a comparison table for clarity:
Student / Office Use
💡 Good value for money
Ideal for office work, web browsing and studies.
Casual Gamer / eSports
🎮 Smooth performance at 1080p
For lightweight and competitive games.
Enthusiast Gamer / 3D Creator
🔥 Performance + AI + durability
Suitable for 3D rendering, editing and AAA games.
AI Professional / Creative
🧠 Best NPU support
Optimised for AI tasks, graphics and productivity.
Mini PCs with Radeon 780M and Radeon 890M (GEEKOM A8 and GEEKOM A9 Max)
iGPUs are now sufficiently powerful for creative and gaming uses. This completely upends the mini PC market. Here are some interesting machines that integrate these chips.
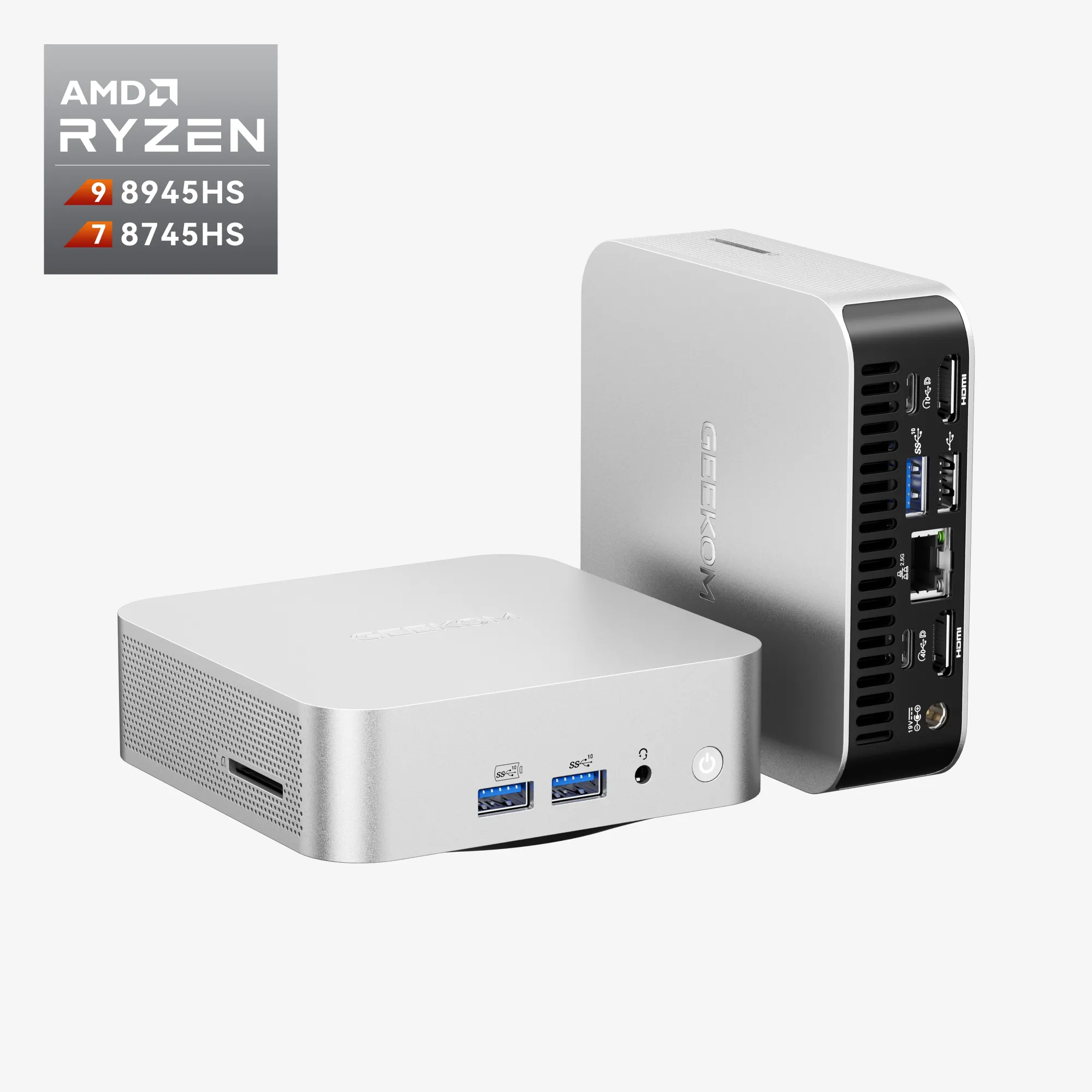
The GEEKOM A8 integrates the AMD Radeon 780M GPU with a Ryzen 9/7 APU (e.g. 8945HS/8745HS). All in an ultra-compact configuration perfectly suited for office work, streaming, light gaming or multitasking.
- AMD Ryzen™ 9 8945HS or Ryzen™ 7 8745HS.
- AMD Radeon™ Graphics 780M
- DDR5 5600MT/s dual channel, up to 64 GB
- SSD M.2 2280 PCIe Gen 4 x 4, up to 2 TB
- Intel® Wi-Fi 6E & Bluetooth® 5.2
- Stunning minimalist design. 0.47 L aluminium casing
- Windows 11 Pro + Copilot AI

For more demanding uses, it’s advisable to turn to the GEEKOM A9 Max. A range that steps up a notch with the Radeon 890M GPU, via the Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 APU. It’s the perfect choice for gamers, creators or AI-friendly users. It also offers high-end connectivity, expandable storage, and multiple display support.
- The AMD Ryzen™ 9 HX 370 mini PC with the best value for money.
- AMD Ryzen™ AI 9 HX 370 | Radeon™ 890M – Up to 80 TOPS AI + powerful graphics for editing and 1080p gaming.
- DDR5 5600 MT/s up to 128 GB | PCIe 4.0 SSD up to 8 TB
- 4 screens up to 8K@120 Hz – 2× HDMI 2.1 + 2× USB4 for maximum productivity.
- Wi-Fi 7 + BT 5.4 + Dual LAN 2.5 Gb/s.
- 8 USB ports + SD + Audio + Kensington.
- Silent cooling – Dual copper heatpipe +52% thermal efficiency.
- Windows 11 Pro + Copilot AI + Linux compatible.
In short, the A8 (780M) is an excellent compromise. Particularly for users looking for a compact and high-performing but affordable mini PC. For those who want to “do everything” (high-performing 1080p games, content creation, AI) the A9 Max (890M) is the model to choose.
Conclusion: A Successful Generational Leap
The comparison between the AMD Radeon 890M vs 780M clearly illustrates the evolution of AMD iGPUs. The 890M, with its 16 compute units, its RDNA 3.5 architecture and its integrated NPU, offers a real performance gain. Particularly for gaming, content creation and local AI processing. Which makes it the benchmark iGPU for 2025.
The 780M, more modest and efficient, remains a relevant choice. Particularly for users who want office fluidity, 4K streaming and light gaming. And this, without compromising on battery life and compactness.
Each GPU therefore has relevance according to profile and needs. Choose GEEKOM, choose the right one, the first step is to know your real needs.