The development of local Artificial Intelligence (AI) is profoundly transforming computing usage. Mini PCs have now become credible alternatives to traditional workstations. More compact, more economical, and quieter, they appeal equally to office professionals, content creators, and edge computing deployments.
In this context, Intel and AMD now integrate Neural Processing Units (NPUs) directly into the heart of their processors. This promises gains in responsiveness and confidentiality, without cloud dependency.
This article aims to evaluate not only the power of these chips, but also the real user experience. Particularly through sustained AI performance, operating costs, maintenance, and long-term sustainability. The analysis is based on concrete scenarios (assisted productivity, generative creation, and continuous inference). These are supplemented by measurements of battery life, noise, temperature, and total cost of ownership (TCO).
How Mini PCs Are Transforming Local AI Usage
The rise of AI has occurred simultaneously with the increasing power of mini PCs. By combining performant processors, dedicated NPUs, and optimised software integration, they offer an alternative that is at once more efficient, more responsive, and more privacy-respecting than cloud solutions. However, their compact format imposes major technical compromises. Particularly regarding sustained power and thermal management.
To properly evaluate the relevance of an Intel Core Ultra or AMD Ryzen AI, it is essential to understand these constraints.
Physical Constraints and Their Consequences
The compact format of mini PCs limits both thermal dissipation capacity and cooling system size. The thermal envelope (TDP) is often between 28 and 45 W on these machines. This dictates how long the processor and NPU can maintain their maximum frequencies.
Under prolonged load, AI performance therefore tends to stabilise at a lower level. Particularly compared to that observed on a laptop or better-ventilated desktop.
This is why chassis design is a critical factor. Well-channelled airflow, effective heat pipes, and judicious fan positioning influence both performance consistency and noise emissions.
Some models use vapour chambers or semi-passive modes to preserve silence. However, this generally comes at the cost of a slight reduction in sustained power.
Finding the right balance between compactness, cooling, and AI performance is one of the challenges of mini PCs.
Different User Priorities vs Desktop/Server
With a mini PC, expectations differ from those of a desktop or server. For many users, such as solicitors or content creators, maximum latency and confidentiality are priorities, rather than hardware capabilities. Having the ability to execute AI models locally guarantees responsiveness. It also avoids transmitting data to the cloud, which is a determining argument in a professional context.
Added to these requirements is the need for compactness and silence. The mini PC must be able to integrate discreetly into an office or studio. And this, without noise pollution. These criteria, based more on comfort and security, modify how users evaluate power. A processor capable of maintaining stable AI performance in a silent and well-cooled chassis will offer a better “real experience”. Particularly compared to a faster chip that is subject to throttling or excessive noise.
Evaluation Framework Specific to Mini PCs (New Protocol)
To compare Intel Core Ultra and AMD Ryzen AI processors in the mini PC arena, one must follow a protocol adapted to their physical constraints and concrete uses. Classic synthetic benchmarks, which focus on TFlops or raw inference times, are no longer sufficient to reflect the real experience of a mini PC user. Nowadays, stability, noise, and perceived responsiveness are just as important as pure power.
We therefore used a precise evaluation framework for our tests. We prioritised use cases, performance consistency, and overall cost of use.
📊 Key Measurements Used
AI Responsiveness
System responsiveness in assistance tasks (Copilot, Office 365, local image generation)
Power Consumption
Average and peak consumption during real sessions to determine NPU/CPU energy efficiency
Thermal Performance
Temperature and thermal ceiling tested under prolonged load (up to 30 minutes of sustained inference)
Noise Level
Measured in decibels at 30 cm from the machine to evaluate cooling system and auditory comfort
Software Integration
Framework support (ONNX Runtime, DirectML, PyTorch), AI assistant optimisation, driver maturity
Updates & Maintenance
NPU update frequency, cooling accessibility, firmware management for long-term reliability
Selected Test Scenarios
We reproduced 4 usage scenarios to get a precise idea of performance:
- Assisted productivity (Copilot and Office): This test measures latency and fluidity of AI assistance in daily tasks. Such as creating texts, translating documents, or summarising emails. The goal is to observe whether the NPU, or CPU, effectively takes over. And this, without any impact on system responsiveness.
- Local generative image AI: Based on Stable Diffusion executed locally. This scenario demonstrates the combined power of the NPU and integrated GPU. It allows testing the mini PC’s capacity to produce quality images fairly quickly. Whilst keeping an eye on temperature and noise.
- Voice inference and instant translation: Simulation of office usage with automatic transcription and instant translation. In this scenario, stable performance and perceived latency matter more than processing capabilities. This is normal because an interruption or delay makes the task impossible.
- Background machine learning tasks: Such as file indexing, contextual search, or semantic recall. These are discreet tasks that are performed continuously. This allows determination of consumption when the machine is idle as well as NPU reliability. But also the system’s capacity to manage multiple loads without overheating or slowdown.
With this protocol, real experience is at the heart of the test. We are not only evaluating power figures. We take into account priorities specific to the mini PC format. Namely: energy efficiency, thermal stability, acoustic comfort, and software sustainability.
Intel’s Approach (Core Ultra): System Integration and Usage Stability
With its Core Ultra generation, Intel focuses on a complete integration strategy. CPU, GPU, and NPU work in synergy within an architecture designed for versatility. Built on the Meteor Lake and then Lunar Lake platforms, these processors embody the desire to offer a fluid and stable AI experience. And this, on any type of machine, including mini PCs.
The objective is not solely to maximise raw performance. The approach also aims to ensure behavioural consistency and exemplary software compatibility. This approach, centred on balance and system mastery, places Intel in a strong position. Particularly for productivity, assistance, and intelligent office uses.
Relevant Characteristics for Mini PCs
On mini PCs, the integrated NPU of Intel Core Ultra (Gen 1 and 2) is distinguished by its stability under prolonged load. Where many compact systems see their AI performance drop beyond a few minutes, Intel chips manage to maintain a constant inference throughput. Particularly thanks to fine TDP management and coordination between CPU, GPU, and NPU blocks.
In public tests conducted on models like the Core Ultra 7 155H (28–45 W), the NPU displays sustained power of approximately 10 to 11 TOPS. With limited thermal degradation after 20 minutes of continuous use. This is quite a remarkable result in a reduced chassis.
This stability is explained by Intel’s integration philosophy. Thanks to coordination between firmware, the Windows scheduler, and the AI driver, loads are distributed intelligently. When the NPU reaches its thermal limits, the system automatically transfers part of the processing to the integrated GPU. An approach that guarantees execution continuity without perceptible latency.
Windows 11 / Copilot optimisations also play a central role. Microsoft collaborates closely with Intel to make the best use of the NPU via Windows Studio Effects and DirectML APIs. This translates into a tangible reduction in perceived latency in assistance tasks. Such as text generation, voice processing, or visual correction in video conferencing.
This consistency between hardware and operating system allows Intel to offer a particularly fluid experience on mini PCs. Machines intended for office environments or noise-sensitive spaces, where resources must be managed with precision.

Intel Strengths on a Mini PC

In the context of mini PCs, one of Intel’s great assets is its thermal and energy management. Adaptive operating modes (“Balanced”, “Cool”, or “Quiet”) adjust CPU/NPU power. And this, according to internal temperature and desired noise level.
On certain OEM models (such as NUC 13 Pro or others equipped with Core Ultra), these modes allow maintaining a temperature below 80°C at full load. But also reducing noise to approximately 32–34 dB(A), a level that is acceptable for a quiet office.
Intel’s eco modes also extend hardware lifespan by reducing electrical load on components. This is an appreciable element in 24/7 installations or edge deployments. Environments where reliability is more important than absolute performance.

On the software side, Intel benefits from maturity superior to AMD’s for everything concerning professional compatibility. The manufacturer has an ecosystem of certified drivers for Windows and Linux, complete support for enterprise deployment tools (vPro, Intel EMA), and regular updates of microcodes and AI firmwares via Windows Update. This continuity reassures IT services as they can keep mini PCs updated without complex manual procedures.
Moreover, Intel works upstream with Microsoft to ensure compatibility of its NPUs with Copilot+ PC. This guarantees transparent integration for users who lack technical skills.
In short, Intel focuses on stability, compatibility, and temperature mastery. Its NPUs do not seek to achieve extreme performance in AI calculation. But they offer a stable and predictable experience. They are therefore perfectly suited to professional sectors where reliability, silence, and energy efficiency are priority criteria.
Read more about: Are There Better Options Than Intel for AI Tasks?
AMD’s Approach (Ryzen AI): Power and Flexibility for Local Creation
With its Ryzen AI range, AMD focuses on software flexibility and creative performance. Processors equipped with the Ryzen AI XDNA engine combine sustained computing power and extended compatibility with open AI software components. This allows developers and creators to execute complex models directly on their machine.
In the context of mini PCs, this option particularly appeals to users oriented towards content creation and visual rendering or local AI experimentation. Sectors where loads are intense but short. Intel emphasises stability and system integration. Conversely, AMD focuses on freedom of exploitation and the capacity to take advantage of all the hardware’s potential. And this, including on compact machines.
Relevant Characteristics for Mini PCs
The XDNA NPU embedded in Ryzen AI processors, resulting from the Xilinx acquisition, is one of the elements that differentiate AMD. Designed around an adaptable architecture, it allows fine distribution of AI calculation between the NPU, Zen 4/5 CPU, and RDNA 3/3.5 GPU. And this, depending on task type. This flexibility proves particularly useful on a mini PC. And for good reason, thermal constraint obliges quick choice between performance and dissipation.
Tests were conducted on compact configurations based on Ryzen 7 7840U and Ryzen AI 9 HX 370. In such situations, the NPU reaches peaks of 12 to 16 TOPS on local inference loads. This is a non-negligible advance over equivalent Intel Core Ultra chips.
However, sustainability strongly depends on cooling. In a well-ventilated chassis, performance remains stable for about fifteen minutes. But NPU frequency can then drop by 10 to 20% to preserve temperature.
The integrated RDNA GPU provides a power complement for mixed AI and graphics loads. During intensive calculation “bursts” (for example, image generation or accelerated 3D rendering), it can take over from the NPU to process heavy convolutional layers. And this, thanks to its optimised vector units. This CPU/NPU/GPU synergy makes Ryzen AI an ideal solution for creation-oriented mini PCs. It is capable of quickly processing occasional high-intensity calculation tasks, such as image generation via Stable Diffusion, video segmentation, or real-time visual effects processing.
For compatibility, AMD focuses on openness. DirectML, ONNX Runtime, and PyTorch benefit from complete support, and development tools (such as ROCm or AMD AI Engine Direct) facilitate implementation on Linux and Windows. For creators and researchers, this software flexibility is a determining advantage. Particularly compared to Intel’s more closed ecosystem.

Read more about: AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 vs Intel Core Ultra: The Battle for AI Mini PC Supremacy
Strengths on Mini PCs
Ryzen AI processors are mainly distinguished by excellent performance in generative AI. Thanks to the combination of XDNA NPU and RDNA GPU, they efficiently process short and intense sessions. Including local image generation, 3D modelling, or texture rendering. This “burst” approach particularly suits users who prefer occasional speed to sustained performance.
Strengths on Mini PCs
Excellent Generative AI
XDNA NPU + RDNA GPU combination efficiently processes short, intense sessions
- → Local image generation
- → 3D modelling
- → Texture rendering
“Burst” Approach
Ideal for users who prefer occasional speed over sustained performance
Perfect for: Quick, intensive tasks rather than continuous workloads
Development Flexibility
Better flexibility for development sectors with open-source focus
- → Native Linux compatibility
- → Docker container support
- → Open-source ML workflows
Moreover, AMD offers better flexibility for development sectors. It offers native Linux compatibility, Docker container support, and easy integration into open-source machine learning workflows. These assets make Ryzen AI mini PCs a natural choice for freelancers, creation studios, and laboratories wanting to experiment locally without cloud dependency.
Specific Constraints
Such performance implies constraints. Temperature must be well controlled to avoid throttling. In more compact machines, insufficient cooling can cause peak performance to drop after 10 minutes of continuous use.
Energy consumption under load is often higher than that of an equivalent Intel Core Ultra. The noise level can therefore be higher (around 36–38 dB(A) depending on models).
These constraints require careful consideration of mini PC design. Particularly for creative uses demanding stability and silence.
Specific Constraints
Temperature Control
Must be well controlled to avoid throttling
Critical: Insufficient cooling can cause peak performance to drop after 10 minutes of continuous use
Higher Power Draw
Energy consumption under load is often higher than equivalent Intel Core Ultra
Increased Noise
Noise level can be higher under load
3 Practical Case Studies
Nowadays, mini PCs with integrated AI processors are no longer limited to demonstration uses. They are used in very varied professional environments. Each chosen scenario illustrates different priorities (confidentiality, creativity, or reliability) that influence the choice between Intel Core Ultra and AMD Ryzen AI. These case studies allow understanding how thermal behaviours, software stability, or calculation flexibility translate concretely into a user’s daily life.
Case A: Law Office: Confidentiality & Productivity
Law Office
Confidentiality & Productivity
🎯 Main Criteria
💼 Typical Use Cases
- Copilot AI assistance
- Document summarisation
- Local data processing (no cloud leakage)
Winner: Intel Core Ultra
Why Intel wins: Deep Windows integration, economical NPU, and stable thermal management for fluid and discreet execution
- Certified drivers & vPro security
- Minimal heat generation
- Silent operation in office environments
- Guaranteed comfort & confidentiality
Case B: Freelance Content Creator: Image Generation and Editing
Freelance Content Creator
Image Generation & Editing
🎯 Main Criteria
🎨 Typical Use Cases
- AI image generation (Stable Diffusion)
- 3D rendering (Blender)
- Video export (DaVinci Resolve)
- Graphic design workflows
Winner: AMD Ryzen AI
Why AMD wins: RDNA iGPU and faster XDNA NPU enable acceleration of graphic renders and creative tasks
- Superior performance for Stable Diffusion, Blender, DaVinci
- Open software component compatibility
- Linux support for personalised workflows
- More responsive for heavy visual renders
Read more: The Best Mini PCs for Photoshop, Adobe Premiere and DaVinci
Read more about: The Best Mini PCs for Photoshop, Adobe Premiere and DaVinci
Case C: Edge Deployment at Point of Sale: Continuous Inference
Edge Deployment at Point of Sale
Continuous Inference
🎯 Main Criteria
🏪 Typical Use Cases
- Payment terminals
- Video flow analysis
- Intelligent display systems
- Continuous operation in confined spaces
Winner: Intel Core Ultra
Why Intel wins: Energy efficiency and thermal stability with eco modes for continuous operation
- Maintains AI performance whilst limiting heat
- Lower noise output for public spaces
- Reduced maintenance requirements
- Better operational longevity
Lifespan, Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), and Scalability
Beyond processing capacity, evaluation of a mini PC must focus on its sustainability and TCO cost. Integrated AI performance is only useful if the system remains reliable, updated, and easy to maintain over several years. For professionals, freelancers, or edge deployments, software and hardware longevity becomes a decisive criterion. It is often even more determining than choosing the fastest processor. We will therefore examine updates, maintenance, and TCO calculation. Thus, you will have an overview for profitable use over time.
Software Updates and Support (Drivers, Security)
The longevity of an AI mini PC largely depends on the frequency and quality of updates. Intel generally offers 3 to 5 years of NPU and CPU support, with certified Windows and Linux drivers, security microcodes, and regular firmware patches.
For its part, AMD offers similar support over the same period. However, availability of optimised drivers for specific AI applications may differ depending on OEMs or open-source software components. These updates affect sustainability. They guarantee compatibility with new versions of AI software, performance stability, and data security. A poorly updated mini PC can quickly become obsolete. And this, even if its raw power remains high.
Consumables and Maintenance (Fans, Thermal Paste)
To preserve AI performance on a compact mini PC, you must carry out regular maintenance. Depending on the environment, fans should be cleaned every 6 to 12 months. This helps avoid overheating and throttling.
Thermal paste applied to the CPU and NPU can degrade after 2 to 3 years. It is therefore necessary to replace it to maintain the best possible performance.
These interventions are simple but indispensable. They extend system lifespan and guarantee performance consistency. Particularly during prolonged inference or local rendering sessions.
TCO Calculation: Purchase vs Operating Cost (Energy, Maintenance, Replacement)
This total cost combines the initial purchase price with recurring expenses over 3 years. For this calculation, one considers electrical consumption (under load and idle), maintenance frequency and cost (cleaning, thermal paste). But also possible replacement of defective components.
Imagine purchasing an Intel Core Ultra or Ryzen AI mini PC at £1,200. With annual consumption of £80 and annual maintenance of £50. With this data, TCO is estimated at £1,490 over three years. This simplified calculation allows concrete comparison of solutions according to their energy efficiency and reliability over time.
GEEKOM IT15 AI Mini PC
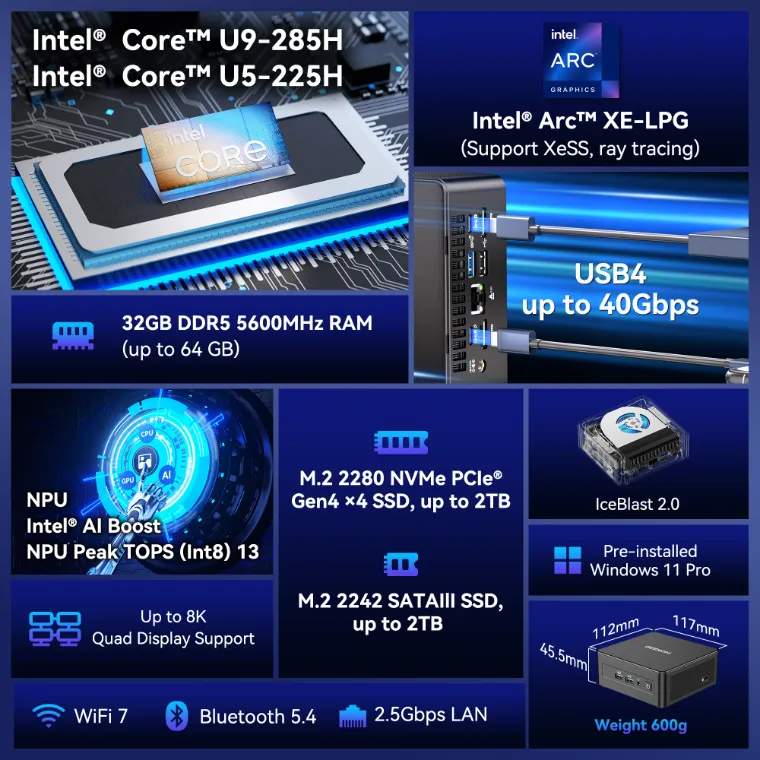
- Intel® Core™ Ultra 9-285H processor and Intel® Arc™ 140T graphics
- High-speed connection: 2.5G Ethernet port, intel® Bluetooth® 5.4 and Wi-Fi 7
- High-speed storage: Equipped with blazing-fast 32GB of DDR5 memory (upgradeable to 64GB) and support for up to 6TB of storage.
- Dual USB4 Ports (Rival OCuLink): Unlock next-generation connectivity. Dual USB4 ports offer Thunderbolt-speed data transfer (40Gbps), dual 8K display output, and support for external graphics cards, effectively replacing OCuLink ports.
GEEKOM A9 Max AI Mini PC

- AMD Ryzen™ AI 9 HX 370 flagship processor and Radeon™ 890M graphics card
- AI: CPU/NPU/GPU triple-engine synergy, up to 80 TOPS computing power, high efficiency, low power consumption, and ultra-fast responsiveness
- High-Speed Storage: Dual-channel DDR5 memory (up to 128GB) and dual M.2 slots (2280+2230) supporting up to 8 TB of PCIe 4.0 SSD storage expansion
- Dual USB4 Ports (Rival OCuLink): Unlock next-generation connectivity. Dual USB4 ports offer Thunderbolt-speed data transfer (40Gbps), dual 8K display output, and support for external graphics cards, effectively replacing OCuLink ports.
Practical Recommendations for Choosing
To choose a suitable AI mini PC, it is essential to select it according to your priorities as a user. Without neglecting the specific constraints of the compact format. Here is a quick checklist that will help clarify your needs before purchase:
- Office professionals: prioritise confidentiality, stability, and silence. Intel Core Ultra mini PCs are generally recommended for these profiles. Particularly for their advanced system integration and mature software support.
- Content creators: AI performance for image generation, video rendering, and intense multitasking. AMD Ryzen AI stands out for its occasional computing power and integrated RDNA GPU. It offers speed and flexibility for creative workflows.
- Developers/researchers: Linux compatibility and open frameworks (ONNX, DirectML, PyTorch), flexibility for containers and local tests. Here, the advantage goes to AMD thanks to its ecosystem openness, whilst remaining viable under Windows.
- On-site data processing/24/7 deployment: controlled consumption, reduced maintenance, and long-term reliability. Intel is often preferred for its stable thermal management and eco modes. Which ensures consistent performance over time.
Discover below a summary table of each solution’s assets:
| Priority | Intel Core Ultra | AMD Ryzen AI |
|---|---|---|
| Confidentiality | ✓✓✓✓✓ | ✓✓✓ |
| AI performance (short bursts) | ✓✓✓ | ✓✓✓✓✓ |
| Silence/comfort | ✓✓✓✓✓ | ✓✓✓✓ |
| TCO/maintenance | ✓✓✓✓✓ | ✓✓✓✓ |
Finally, discover our purchase advice for a better experience on an AI mini PC:
- Chassis and cooling: opt for models offering effective thermal dissipation and optimised airflow.
- Software certifications: verify Copilot/Windows compatibility as well as availability of certified drivers.
- Fan accessibility: choose a case where cleaning and replacement of critical components are simple. This will allow you to extend lifespan and maintain performance.
Dedicated GPU or Integrated NPU: Which Choice for Your AI Needs?
Dedicated GPU or Integrated NPU: Which Choice for Your AI Needs?
Integrated NPU
- ✓ Intel Core Ultra processors
- ✓ AMD Ryzen AI processors
- ✓ Suited to most mini PCs
- ✓ Ideal for standard workloads
Dedicated GPU/NPU
- ✓ Better performance
- ✓ No thermal/frequency limits
- ✓ Enhanced stability
- ✓ Lower noise levels
! When Dedicated GPU/NPU is Justified
Heavy, Repetitive Loads
Continuous processing that pushes CPU limits
Short Inference Times
Training complex AI models efficiently
3D Rendering
High-resolution graphics processing
Video Inference
Continuous real-time video analysis
🔄 Hybrid Approach: Best of Both Worlds
Combine compact mini PC with external accelerator for occasional calculation peaks
Mini PC (Integrated NPU)
- → Daily processing
- → Short local tasks
- → Compact & silent
- → Energy efficient
External GPU/NPU
- → Heavy renders
- → Batch inferences
- → Peak workloads
- → Maximum power
Real-World Scenarios
Content Creator
Industrial IoT
✨ Benefits of Hybrid Approach
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is impossible to designate Intel Core Ultra or AMD Ryzen AI as superior on all levels. The choice depends above all on the usage context and your priorities as a user. For professional environments where confidentiality, silence, and stability are essential, Intel often proves the most suitable solution. Conversely, for creators and developers seeking occasional power, software flexibility, and open-source compatibility, AMD has the advantage.
On a mini PC, thermal management, noise pollution, and software support maturity are as important as the NPU’s pure power. A fast processor, but poorly cooled or poorly supported, quickly loses its interest in daily use.
Finally, more efficient NPUs as well as more economical processors are expected in the future. There is good reason to believe that interoperability standards will also be reinforced. Changes that promise even more accessible and performant local AI on compact workstations.
FAQ on AI PCs
Can a mini PC without NPU remain useful for local AI?
Yes, but performance will be limited to classic CPU/GPU. Light AI tasks or inference of small models remain possible. However, in case of intensive loads, the experience will be slower and less efficient.
Can one replace a mini PC’s cooling to improve AI?
Yes, it is possible on certain models. You can replace or optimise fans and thermal paste. One should know that better cooling can help reduce throttling. This extends sustained CPU/NPU power.
How can I measure if a mini PC will throttle on my AI tasks?
To measure if a mini PC will throttle, monitor CPU/NPU temperature and frequency during prolonged load. You can use a tool like HWInfo or Ryzen Master/Intel XTU. If frequency drops quickly under load, then your mini PC risks throttling on your tasks.