This is a big change for mini PCs. The once-boring computers used in offices have become surprisingly powerful little machines that can run real AI programs. You are discussing two very different ideas: While AMD focuses on raw power, Intel is smartly using modules to make their products.
In this case, the comparison is more important than usual. If you pick the right chip, your next mini PC will be able to run AI models locally, improve video in real time, or handle that language mode, which you want to try without having to send everything to the cloud. Each company knows what is at stake and has done what it could.
The Competitors: What You’re Actually Getting
When you look at the specs side by side, you can see how differently these companies think about the problem. AMD went for brute force. Intel went for flexibility.
AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370: The Heavy Hitter
The best chip from AMD gives mini PCs a lot of power. Utilising TSMC’s 4nm process, they packed in 12 cores, with 4 being fast and 8 being efficient. The fast cores can go as fast as 5.1 GHz when they need to, but the 3.3 GHz top speed is the fastest they can go.
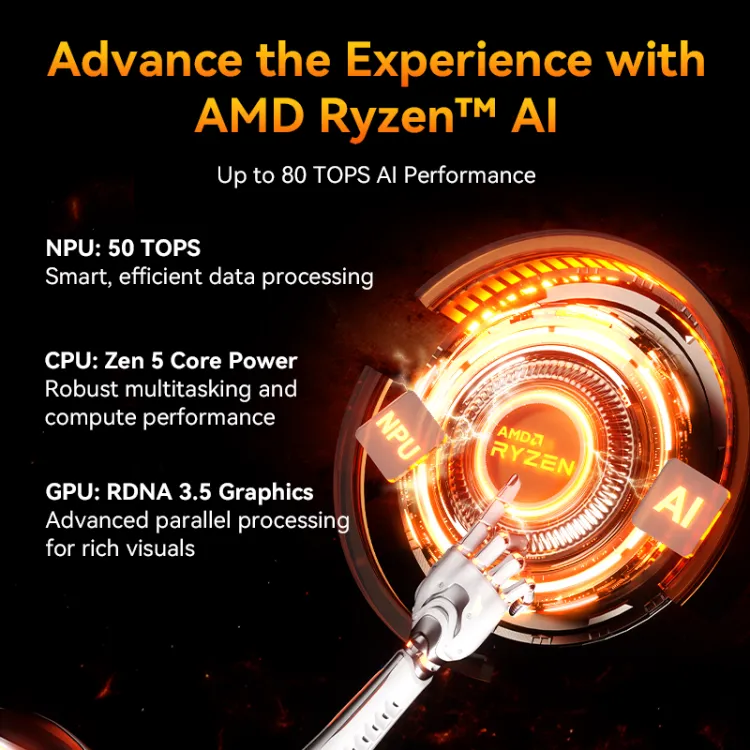
The XDNA2 NPU from AMD makes 50 TOPS for AI work. That is more than four times what Intel is in charge of. The graphics card is a Radeon 890M, which is based on their RDNA 3.5 design and can run at up to 2900 MHz.
| AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 | What You Get |
|---|---|
| Architecture | Zen 5 (Strix Point) |
| Manufacturing | 4nm TSMC |
| Cores/Threads | 12C/24T (4P + 8E) |
| Clock Speeds | 2000 MHz / 5.1 GHz |
| Power Draw | 28W (15-54W range) |
| AI Muscle | 50 TOPS (XDNA2) |
| Graphics | Radeon 890M (RDNA 3.5) |
| Memory | DDR5/LPDDR5X-5600 |
| Release | July 2024 |
Intel Core Ultra: The Clever Alternative
With Meteor Lake, Intel took a very different path. Instead of making one big chip, they used four different manufacturing methods to make four different chips. It has Intel’s 7nm process for the main CPU part and TSMC’s better processes for the graphics and other parts.
The Ultra 7 155H takes more work to set up the cores. There are 6 fast cores, 8 regular efficient cores, and 2 super-low-power cores for background tasks. The quick cores can go up to 4.8 GHz, and the quick cores can go up to 3.8 GHz.
That is a lot less than AMD, whose AI Boost NPU does 11 TOPS. Their Arc Xe-LPG graphics card has 128 execution units that run at 2250 MHz.
Based on these specs, it is clear that AMD cared more about AI power than Intel did, which cared more about having more cores with different strengths. Both aim for the same 28W power budget for mini PCs, but they do it in very different ways.
If you always want the best, Intel’s Core Ultra 9 185H is for you. Intel’s flagship processor takes everything you love about Meteor Lake and turns it up to eleven.
The same smart 16-core hybrid design, but Intel has selected the best silicon and pushed P-cores to 5.0 GHz. That means you will notice the difference immediately when crushing single-threaded tasks or needing a boost. The 45W base TDP shows Intel designed this chip for mini PC users who want maximum performance.
That configurable TDP can reach 115W, which is interesting for mini PC fans. If you build or buy a premium compact workstation, you can get desktop-class performance in a form factor that fits on your desk. Most mini PCs will not let you use all that power. You get flexibility that expands your mini PC’s capabilities, not just a faster processor.
| Intel Core Ultra | Ultra 7 155H | Ultra 9 185H |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Meteor Lake | Meteor Lake |
| Manufacturing | 7nm Intel + TSMC pieces | 7nm Intel + TSMC pieces |
| Cores/Threads | 16C/22T (6P + 8E + 2LP) | 16C/22T (6P + 8E + 2LP) |
| Clock Speeds | 3.8 GHz / 4.8 GHz | 3.8 GHz / 5.0 GHz |
| Power Draw | 28W (up to 115W burst) | 45W (up to 115W burst) |
| AI Muscle | 11 TOPS (AI Boost) | 11 TOPS (AI Boost) |
| Graphics | Arc Xe-LPG 128EU | Arc Xe-LPG 128EU |
| Memory | DDR5/LPDDR5X-5600 | DDR5/LPDDR5X-5600 |
| Price | £375 | £435 |
Click to read more about Intel Core Ultra 9 285H vs AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370: The Ultimate 2025 Showdown
Mini PC Reality Check
Building a mini PC is not like building a desktop, where you can put a big cooler on top of it. You have to work in a small area, which changes how these chips work in every way.
Heat Management Headaches
It is important to keep mini PCs cool. When you put that 28W into something the size of a small book, it does not sound like much. It works differently on each chip.
AMD’s single-piece design heats up more, but the 4nm process makes it more efficient. From 15W to 54W, manufacturers can tune for either top speed or quiet operation.
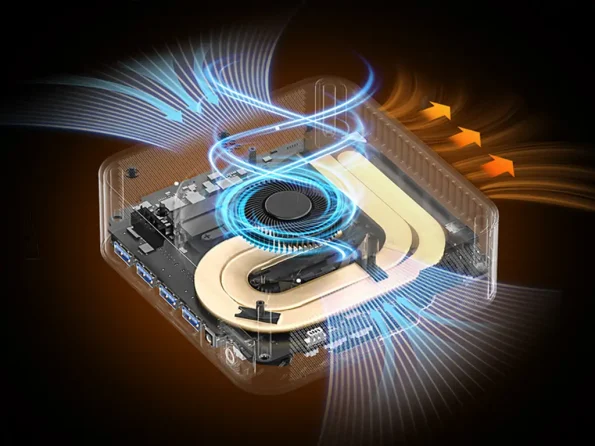

Intel’s tile method makes the package cooler all over. On TSMC’s process, the separate graphics tile can stay cooler than integrated solutions. However, the complicated package makes it harder to keep cool.
Read more: Water Cooled PC Vs Air Cooled PC: Make A Wise Choice
What Happens Under Load
You need to know this before you buy a mini PC. Those peak numbers look great, but what about after working hard for 10 minutes?
AMD‘s efficient cores that run at lower base speeds (1400 MHz) suggest that this was made for long-term use. Due to the wide power range, manufacturers can make any type of system, from a 15W box with no fans to a 45W system with fans and active cooling.
Intel‘s choice to have more cores but weaker AI suggests that they think the CPU will be able to handle AI work in the long term. Its maximum power of 115W shows that this chip can go much higher when it has enough room to cool down.
CPU Speed Comparison
Which one actually runs faster? Depends on what you’re doing with it.
Single-Core Work
Intel has a small edge for tasks that only use one thread because its boost clocks are higher. The Core Ultra 7 155H’s 4.8 GHz and the HX 370’s 5.1 GHz make for an interesting comparison: AMD’s faster peaks and Intel’s more refined architecture.
Both chips work great for single-threaded mini PC tasks in real life. You will not notice any big differences when you browse the web, do office work, or write light content.
Multi-Core Work
This is where the differences in the architecture become clear. With 12 cores and SMT, AMD gives you 24 threads, and Intel gives you 22 threads with 16 cores.
AMD’s method usually works best for making content that can use all available threads. Powerful Zen 5 cores and fast background processing make encoding videos, rendering 3D models, and putting together videos a breeze.
Intel’s hybrid design works great for mixed workloads where you need to do responsive work in the foreground while tasks keep running in the background. Separated low-power cores take care of system maintenance without affecting your main programs.
Graphics Showdown
Gaming on mini PCs has gotten surprisingly good, and both chips bring real graphics muscle.
Graphics Architecture Differences
The Radeon 890M from AMD uses their newest RDNA 3.5 architecture, which is much better than older generations. The boost clock of 2900 MHz gives the computer a lot of power for 1080p gaming.
With 128 execution units, Intel’s Arc Xe-LPG graphics is its most serious attempt to make integrated graphics that can compete. The TSMC process’s 2250 MHz speed and dedicated graphics tile make it work well.
Gaming Reality
Tom’s Hardware reported that AMD said its Core Ultra 7 258V was 75% better for gaming than Intel’s. These numbers come from AMD’s own tests with the best settings, and they clearly show that the Radeon 890M is much better in graphics-heavy programs.
When playing games in real life at 1080p medium settings, both chips can easily handle e-sports games and older AAA games. For new games that are hard to play, you may need to change the settings or look into external graphics.
AI Acceleration Battle

Now things really start to get interesting. Both companies have put a lot of money into AI workloads, which are the future of computing.
NPU Architecture Breakdown
AMD’s XDNA2 NPU, which has 50 TOPS, is a huge step forward for AI on the device. With this much power, you can do local LLM inference, real-time image processing, and advanced video enhancement without having to depend on the cloud.
When it comes to AI, Intel’s AI Boost NPU at 11 TOPS is more cautious. It is not nearly as powerful as AMD’s solution, but it is meant to work with both the CPU and GPU for distributed AI processing.
AI Workload Reality
When doing local LLM inference, AMD’s NPU advantage is clear right away. To run models like Llama 2 7B or similar locally, you need 50 TOPS of dedicated AI power. Although Intel’s method requires more CPU work, it slows down the system as a whole.
Image processing and creation tasks work best with AMD’s AI hardware. The XDNA2 NPU powers better real-time video enhancement, background removal, and other related tasks.
Software Support
Intel’s longer history in AI means that more software will work with it at first. Apple has optimised the code paths for Windows Copilot+ features and many AI frameworks.
For best results, AMD’s newer XDNA2 architecture needs software updates, but the raw computational advantage often makes up for optimisation gaps. Framework support keeps getting better quickly.
Power and Heat Management

People who buy mini PCs care a lot about how much power they use and how much heat they generate. It is not nice to have a space heater on your desk.
Both chips aim for the same 28W power budget, but they are very different in how efficient they are. Intel’s tile-based design allows for more precise power management, while AMD’s 4nm process is naturally more power-efficient.
AMD’s range of 15–54W and Intel’s range of 28W base and 115W maximum power tell the story. AMD made their processors to be flexible across a range of temperature ranges, while Intel made their processors faster when cooling is possible.
Real-World Mini PC Uses
Let’s talk about what these chips actually mean for your mini PC use cases.
Content Creation Workstation
When you combine AMD’s fast CPU with its powerful NPU, you get clear benefits for creative tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, and more. It is really helpful to be able to send AI-enhanced video processing to separate hardware while keeping the CPU speed for timeline scrubbing and effects processing.
Intel’s approach works well for creative work that is not too heavy, since the extra CPU cores can handle a variety of tasks well. For streaming and making videos, the Arc graphics cards have good hardware encoding options.

AI Development Platform
AMD’s 50 TOPS NPU advantage is very important when you are making AI apps or running local models. Iterating on AI models locally, without having to depend on the cloud, speeds up development workflows by a lot.
However, Intel’s platform needs better resource management to be useful for AI development. AI tasks will have to rely more on CPU and GPU resources because the NPU is slower.
Gaming and Entertainment Hub
Both chips can handle 1080p gaming well, but AMD’s graphics are better for games that need more power. A gaming platform that is well-balanced combines a fast CPU with good built-in graphics.
Intel’s solution works well for esports and older games, and it is compatible with more games because it has been on the market longer.
Platform Ecosystem and Vendor Support
The chip you choose affects more than just speed; it affects everything about your mini PC. When you are making a system that needs to work well for years, this is more important than you might think.
Motherboard Availability and Vendor Adoption
A lot of mini PC makers have quickly switched to AMD’s Socket FP8 platform. Companies like ASUS, MSI, and custom mini PC builders have jumped on the HX 370 because of its powerful AI features. The problem is that the platform is still pretty new; you are working with first-generation implementations that might have some bugs.
Because Intel has been in the mobile market longer, more vendors support its BGA 2049 socket. More manufacturers make mini PCs based on Meteor Lake, so you have more options in terms of size, price, and cooling. It is easier to make sure that everything works with the mature platform.
Memory and Storage Considerations
In theory, both chips can handle DDR5 and LPDDR5X memory up to 5600 MT/s, but in practice, how they work on different platforms is very different. While AMD’s memory controller works well with fast DDR5 kits, Intel’s version needs more conservative timings for stability, some of the time.
Similarly, storage support tells the tale. Both platforms let NVMe SSDs connect via PCIe 4.0, but Intel’s tile-based design has more PCIe lanes overall. If you want to build a mini PC with multiple fast storage devices or an external GPU, this is important.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Price matters, especially in the mini PC market, where value optimisation drives many purchasing decisions.
Total Cost of Ownership
The Core Ultra 7 155H from Intel has a higher MSRP of £375 than AMD’s usually lower prices, which creates different value propositions. However, platform costs, power use, and the amount of cooling needed all affect the total cost of ownership.
Over time, AMD’s lower power use in many workloads could lower electricity costs, while Intel’s wider ecosystem support could lower the costs of accessories and peripherals.
Speed Per Dollar
When you look at speed per dollar, AMD’s faster CPUs and better AI capabilities often make it a better deal for AI-focused apps. Intel has an advantage because its platforms are more mature and work with more devices.
The calculation changes based on how you plan to use it. For AI development, AMD’s NPU advantage is worth the extra cost. Intel’s wider range of features might be a better overall value for general computing with some AI tasks.
The Verdict: Picking Your AI Mini PC Champion

- Performance: AMD Ryzen™ AI 9 HX 370 flagship processor + Radeon™ 890M graphics card
- AI: CPU/NPU/GPU triple engine synergy, up to 80 TOPS computing power, high efficiency, low power consumption, and ultra-fast response
- Storage: Dual-channel DDR5 memory (up to 128GB) and dual M.2 slots (2280+2230) for up to 8 TB of PCIe 4.0 SSD storage expansion
- Fast connectivity: Dual 2.5G Ethernet ports, Intel® Bluetooth® 5.4 and Wi-Fi 7
- Efficient heat dissipation: Innovative and Efficient Cooling System – IceBlast 2.0
The choice between these chips is completely up to you based on your needs and priorities.
If you need the most AI power, want to run local LLMs, or need the best built-in graphics, choose AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370. The 50 TOPS NPU and Radeon 890M work well together to make a powerful package for AI-focused apps and games.
Choose the Intel Core Ultra 7 155H if you want more software compatibility, the most CPU cores for a variety of tasks, or guaranteed platform stability. The mature ecosystem and hybrid architecture are great at routine computer tasks.
It is only the beginning of the mini PC revolution, but both chips are big steps forward in the small computer world. Which method works best for you will depend on your specific needs, but both provide real AI acceleration in a surprisingly small package.
It is not just about specs in this race to be the best AI mini PC; it is also about letting new ways of computing work in places where regular desktops will not fit. Both AMD and Intel have made great solutions, but AMD has a clear edge when it comes to the AI-first apps that will define the next generation of computing because it focuses on making hardware just for AI.