In the constantly advancing landscape of computer technology, the need for compact and efficient systems has led to the emergence of Mini-PCs and Thin Clients.
These two solutions offer unique advantages in various contexts, but understanding their differences is crucial for informed decision-making.
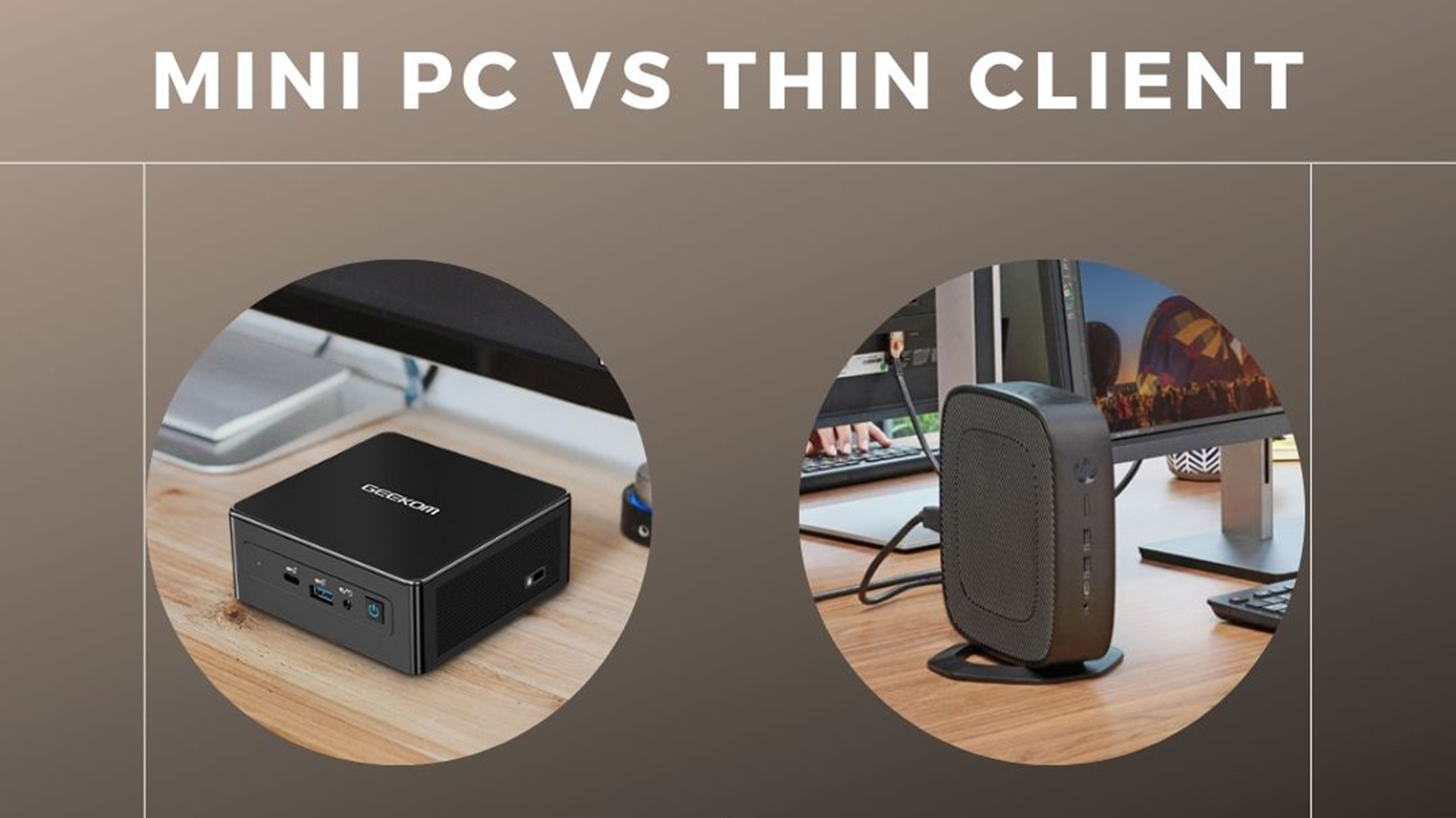
What is a Mini-PC?
A Mini PC, as the name suggests, is a compact computing device that provides the functionality of a desktop computer in a small form factor.
These devices are typically small enough to fit in the palm of your hand, making them highly mobile and space-saving.
Mini-PCs often come with a built-in processor, RAM, storage, and ports for peripherals such as monitors, keyboards, and mice.
What is a Thin Client?
On the other hand, a Thin Client is a lightweight computer terminal that relies on a central server or cloud infrastructure for processing power and storage.
Thin Clients are designed to be simple, cost-effective devices primarily serving as a means to access applications and data stored on a remote server.
In contrast to Mini-PCs, Thin Clients lack powerful internal components and depend on network connectivity for their operation.
Mini-PC vs Thin Client: Features and Performance
Processing Power
Mini-PCs typically come equipped with powerful processors that rival those in full-sized desktop computers. This enables them to handle resource-intensive tasks such as multimedia editing, gaming, and other demanding applications.
On the other hand, Thin Clients have limited processing power due to their primary function of offloading processing tasks to the central server. They are designed for light computer applications like web browsing, document editing, and accessing cloud-based applications.
Storage Capacity
Mini-PCs often provide ample storage options, including Solid-State Drives (SSDs) and Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), allowing users to store a significant amount of data locally.
In contrast, Thin Clients typically have minimal local storage as they rely on the server for data storage. The focus is on accessing data from the server rather than storing it locally.
Graphics Performance
Due to their compact size and powerful internal components, Mini-PCs are equipped with powerful graphics cards. Some may even support dedicated graphics cards, providing excellent graphics performance for tasks like video editing, gaming, and graphics-intensive applications.
Thin Clients, on the other hand, rely on the graphical processing capability of the server, making them better suited for tasks that do not require high-end graphics.
Connectivity Options
Mini-PCs feature a variety of connectivity options, including USB ports, HDMI, DisplayPort, and WLAN, allowing users to connect various peripherals and accessories.
Thin Clients typically have fewer connectivity options as most processing and data transfer operations occur over the network.
Energy Efficiency
Thin Clients are known for their energy efficiency as they consume less power compared to Mini-PCs. This is because processing tasks are shifted to the server, which bears the majority of the power consumption.
Mini-PCs, although more powerful, consume more energy due to their standalone processing capabilities.
Mini-PC vs Thin Client: Use Cases
After exploring the features and performance aspects, let’s now examine the specific use cases and benefits of Mini-PCs and Thin Clients.
Use Cases for Mini-PCs
- Home Entertainment: Mini-PCs can serve as media centers, providing a compact solution for streaming movies, music, and gaming on a large screen.
- Office Productivity: With their powerful processors and storage options, Mini-PCs are ideal for productive tasks such as word processing, spreadsheet work, and presentation creation.
- Creative Work: The graphic capabilities of Mini-PCs make them suitable for graphic design, video editing, and other creative applications.
- Gaming: Mini-PCs with advanced graphics cards offer a convenient gaming platform for casual and moderate gamers.
Use Cases for Thin Clients
- Business Environments: Thin Clients are often used in business environments where multiple users need access to centralized applications and data.
- Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI): Thin Clients are an integral part of VDI solutions, enabling organizations to provide secure and centrally managed desktop environments.
- Remote Work: With the rise of remote work, Thin Clients offers a secure and efficient way for employees to access company resources from any location.
Conclusion
In summary, Mini-PCs and Thin Clients serve different purposes in the computer world, meeting the diverse requirements of users.
The choice between Mini-PCs and Thin Clients ultimately depends on the specific needs and use cases of individuals or organizations.
If you are considering investing in a Mini-PC, I recommend taking a look at the GEEKOM collection. We offer a wide selection of Mini-PCs with various specifications and features to meet different requirements.