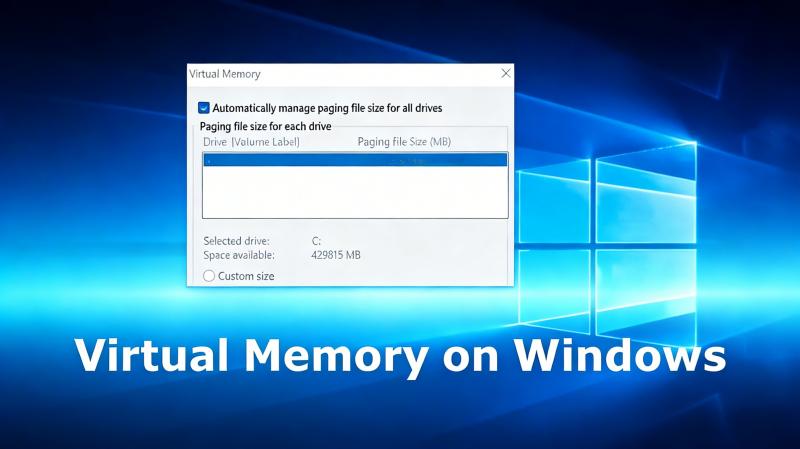
When using your computer, you may encounter warning messages on screen such as “scratch disc full“, “memory or paging error“, or “virtual memory problem in Photoshop“. In these cases, your device may slow down considerably, causing open applications to freeze or even shut down without warning.
These problems occur when virtual memory—the disc space that extends RAM via the page file—is insufficient for all your tasks.
Very often, simply increasing virtual memory and configuring it correctly is enough to resolve the slowdown and allow you to continue using your PC without freezing.
In this guide, we shall explain how to enable and configure virtual memory on Windows 10 and 11, how to speed up your PC, how to avoid messages like “scratch discs full“, and how to better manage both RAM and page files.
Virtual Memory and Virtual Address Space: What Is It? Why Is It So Important?
Virtual memory is the disc space that Windows uses when physical RAM is insufficient; it functions like a much slower extension of RAM, useful for preventing applications from crashing when physical memory runs out. Computer memory refers to the hardware devices (such as RAM) that store data and instructions for processing, and virtual memory is a core memory management technique that abstracts actual memory (physical RAM) and main memory, allowing the operating system to manage resources more efficiently.
We can imagine RAM as the main river through which all active data flows, and virtual memory as a secondary channel that temporarily holds the overflow of information. The basic idea behind virtual memory is that the operating system can extend physical RAM by using secondary memory (such as HDDs or SSDs) as an overflow area, creating a larger address space for programs to use.
When RAM is nearly full, Windows frees up space by reducing the amount of active memory assigned to processes and moving less-used sections to the disc, through techniques such as paging, memory compression, working set trimming, and priority adjustment. The operating system presents an abstract, contiguous address space to each program, which includes both physical and virtual RAM, enabling each process to have its own unique virtual address space mapped onto actual memory and secondary memory as needed.
It should be emphasised that virtual memory does not improve computer speed: its sole purpose is to prevent the system from freezing or shutting down when available RAM is insufficient. The primary benefits of virtual memory include increased security due to memory isolation and the ability to share memory used by libraries between processes. However, virtual memory can lead to performance degradation due to increased access times when data is swapped between RAM and disk storage.
How Virtual Memory Works on Windows 10 and 11
Windows uses RAM as the primary working area, managing all processes and data. Modern operating systems and hardware use memory mapping to translate virtual addresses into physical addresses, a process known as address translation. The Memory Management Unit (MMU) translates virtual addresses generated by the CPU into physical addresses, using page tables and page table entries to manage this mapping. Logical memory is the abstraction that appears as primary memory to the user, even though it may reside on secondary storage or disk storage. Process memory is managed through techniques like paging and segmentation, and each process has its own virtual address space, which is a logical, contiguous range of memory addresses perceived by the application.
When RAM fills up, the system compresses some pages in memory, reduces the space allocated to less active processes, and moves infrequently used pages to the disc (pagefile.sys). This disk storage (secondary storage) acts as an extension of system memory, and the swap file is used to store pages that are not currently in real memory. Virtual RAM (virtual storage) is created by mapping virtual addresses to physical memory and disk storage, allowing the system to use more memory than is physically available. Paging divides memory into small fixed-size blocks called pages (usually 4K in size), while segmentation divides virtual memory into segments of different sizes, allowing for more efficient memory allocation. Paging can lead to internal fragmentation, where some space in the page is wasted, while segmentation can lead to external fragmentation, where small chunks of memory are scattered within the memory space. When the system runs out of RAM, pages that aren’t currently in use are moved to a swap file on the hard drive. Memory regions and table entries in page tables play a crucial role in address translation and memory protection, defining which memory addresses can be accessed by processes.
For optimal performance, Windows automatically calculates the ideal page file size based on requirements.
In this way, Windows 10 and 11 virtual memory functions as a genuine extension of RAM, making the system more stable and fluid, even when physical memory is limited, and you have considerable work to do.
When Should You Increase or Enable Virtual Memory?
Increasing or enabling virtual memory is useful if your computer is slow, freezes, or displays messages like “scratch discs full” on Windows 10/11, or when applications such as Photoshop report virtual memory problems. These issues can occur when the allocated memory for user processes and other programs exceeds the available system memory.
Modern hardware and operating systems support virtual memory, enabling better management of storage space and memory allocation. Increasing virtual memory is especially important when system memory is limited, and storage space is available for the page file.
Note: On Windows 11, memory management is more efficient than on Windows 10, but page file behaviour is similar in both versions.
It is essential to carry out these operations on PCs with limited physical memory (4 to 8 GB) or when using resource-intensive programmes for video creation or editing.
To address these scenarios, GEEKOM mini PCs are particularly useful: thanks to the ability to add RAM and their ultra-fast NVMe SSDs, they can handle many different situations, from everyday use to heavy workloads, reducing the typical slowdowns of older computers and making virtual memory management more effective.
How to Enable and Configure Virtual Memory on Windows 10 and 11
Now we shall show you how to enable and configure virtual memory on Windows 10 and 11. Configuring virtual memory settings allows users to manage how memory addresses and address space are allocated between RAM and disk storage. Note that in Windows, users can adjust virtual memory settings through the performance options in the settings menu. Remember that on Windows 11, the system manages the page file more autonomously, so you may not need to do anything, whilst on Windows 10, manual intervention is often recommended.
Find the Windows Virtual Memory Settings
|
1
|
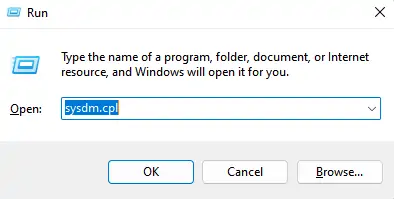
Press the Windows + R keys together → the Run dialog box will appear. |
|
2
|
Type sysdm.cpl and press Enter → System Properties will open. |
|
3
|
Navigate to the Advanced tab → then Performance → and finally Settings. |
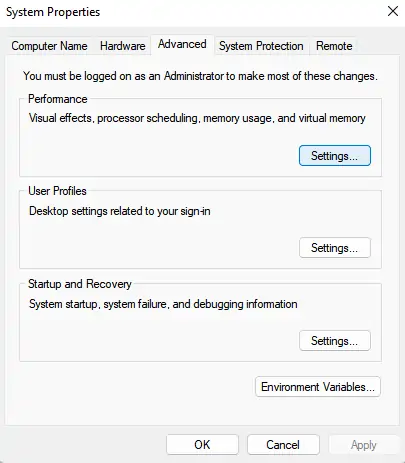
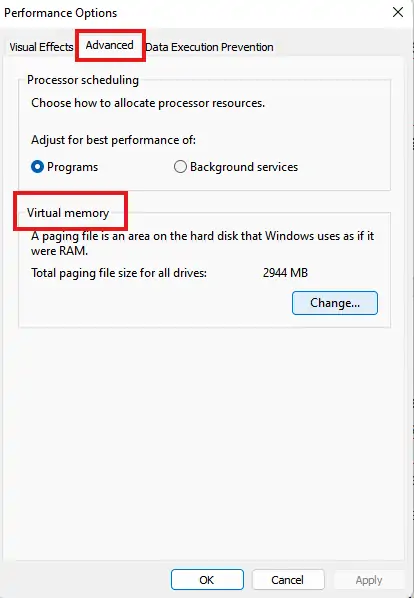
This will take you to the general performance options, where you can manage virtual memory on Windows 10 and Windows 11.
- Access the Virtual Memory Options
- In the Advanced tab, click on Virtual Memory → then Change.
- Untick “Automatically manage paging file size for all drives” (this disables automatic Windows page file management).
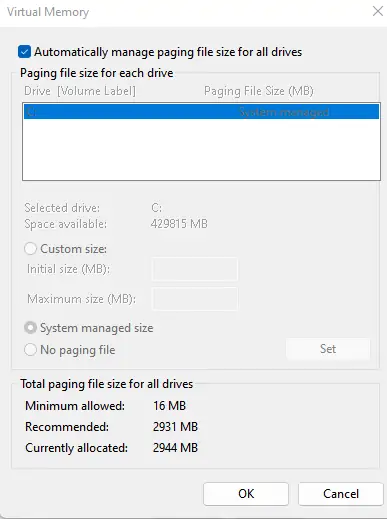
This allows you to manually set the page file size, useful for increasing virtual memory and avoiding errors such as “insufficient virtual memory”.
Note: On Windows 11, this operation is optional as the system manages virtual memory more efficiently on its own; however, on Windows 10, it is recommended to prevent slowdowns on computers with limited RAM.
Select the Drive and Define the Values
Choose the fastest available storage medium:
- NVMe SSD (page file on NVMe SSD) → provides the best speed
- SATA SSD (page file on SSD) → acceptable as a second choice
- HDD (Hard Disc Drive) → use only if you have no SSD available
Set the Windows virtual memory size based on how much primary memory (random access memory, or RAM) you have installed:
- Minimum = RAM × 1.5 (the recommended minimum virtual memory)
- Maximum = RAM × 3 (the recommended maximum virtual memory)
For example: If you have 8 GB of RAM → set the minimum to 12 GB and the maximum to 24 GB.
These values are determined by the amount of primary memory (RAM) in your system. However, the available storage space on the selected drive will also limit how much virtual memory you can allocate.
These are merely guidelines: the correct amount of virtual memory varies depending on how you use your PC and how much free disc space you have.
Note: The same rules apply to Windows 10 and 11, though the newer version manages virtual memory better if you have sufficient RAM (8 GB or more), making the action less essential on Windows 10 or when memory is scarce.
- Apply and Restart
- Press Set → then OK → and finally Restart the computer.
- Now Windows will use pagefile.sys in the best way, making everything more stable and faster, even when you are multitasking or using programmes that consume a great deal of virtual memory.
Additional tip: Always keep at least 10–20% of the disc space free on the drive you have chosen, to avoid ending up with full scratch discs, which causes virtual memory errors or slowdowns.
After making these changes, your PC will be more reliable and faster, making the most of both RAM and virtual memory, even with demanding programmes such as Photoshop.
Virtual Memory Techniques: Strategies for Different Use Cases
Modern operating systems rely on a variety of virtual memory techniques to make the most of available physical memory and ensure smooth multitasking, even when running multiple programs or resource-intensive applications. Understanding these strategies can help you appreciate how your computer manages memory space and why certain settings or upgrades can have a big impact on system performance.
One of the most widely used techniques is demand paging. With demand paging, the operating system only loads memory pages into physical RAM when they are actually needed by a process. This approach keeps memory usage efficient, as only the required data is present in physical memory at any given time, reducing unnecessary memory allocation and helping to prevent memory fragmentation. Demand paging also minimises the number of page faults, which occur when a process tries to access memory that isn’t currently loaded.
Another powerful memory management technique is copy-on-write. This method allows multiple processes to share the same physical memory pages for as long as the data remains unchanged. If one process needs to modify the shared data, the operating system creates a private copy for that process, ensuring memory isolation and data integrity. Copy-on-write is especially useful for launching multiple instances of the same program or when processes need to access the same file, as it conserves physical RAM and reduces overhead.
To keep physical memory from filling up, operating systems use page replacement algorithms. The least recently used (LRU) algorithm is a common choice, as it tracks which memory pages haven’t been accessed in a while and swaps them out first when more memory is needed. This helps maintain optimal memory usage and keeps the system responsive, even under heavy workloads.
Memory allocation strategies also play a key role in virtual memory management. Some systems use fixed allocation, assigning each process a set number of physical memory frames, while others use dynamic allocation, adjusting the number of frames based on the process’s current needs. The best approach depends on your use case: real-time systems may require predictable memory allocation for fast responses, while general-purpose computers benefit from dynamic allocation to maximise throughput and flexibility.
Hardware configuration can influence which virtual memory techniques are most effective. Systems with large amounts of physical RAM might use larger page sizes to reduce the overhead of managing the page table, while those with limited RAM may opt for smaller pages to avoid wasting memory. Fast storage devices, like NVMe SSDs, allow for more aggressive paging strategies, as the speed of reading and writing to disk is much higher than with traditional hard drives.
By understanding and applying these virtual memory techniques, you can optimise memory management, support multiple processes efficiently, and ensure your computer system delivers the best possible performance for your specific needs.
Troubleshooting Virtual Memory Issues
Even with the best virtual memory management techniques, issues can arise that impact your computer’s performance. Knowing how to identify and resolve these problems is essential for maintaining a stable and responsive system.
One of the most common virtual memory issues is thrashing. This happens when your system spends more time swapping data between physical memory and the page file than actually running programs. Thrashing is often a sign that your computer is running out of physical RAM, or that too many applications are open at once. To resolve thrashing, consider closing unnecessary programs, increasing your physical RAM, or adjusting your virtual memory settings to better match your workload.
Page faults are another frequent concern. A page fault occurs when a process tries to access a memory address that isn’t currently loaded in physical memory. While occasional page faults are normal, a high rate can slow down your system and indicate problems with memory allocation or disk space. To troubleshoot, check your system’s page table entries for errors, ensure you have enough free disk space for the page file, and verify that your storage devices are functioning properly.
Memory leaks can also cause virtual memory issues. These occur when applications fail to release memory they no longer need, gradually consuming all available memory and leading to slowdowns or crashes. Developers can use memory debugging tools to identify and fix leaks, while users can monitor memory usage in Task Manager and restart problematic applications as needed.
To keep your system running smoothly, regularly monitor your virtual memory usage using built-in tools like Task Manager or Resource Monitor. Look for signs of excessive page file usage, high memory allocation, or disk activity related to the page file. If you notice persistent issues, try adjusting your virtual memory settings—such as increasing the page file size or moving it to a faster storage device—to improve system performance.
In summary, effective troubleshooting of virtual memory issues involves monitoring physical memory and page file usage, optimising memory allocation, and ensuring your storage devices are healthy. By taking a proactive approach to virtual memory management, you can prevent slowdowns, crashes, and other disruptions, keeping your computer system running at its best.
Advanced Tips to Improve Virtual Memory
It is essential to keep at least as much free space as the page file size you have set, plus approximately 20%, because when space runs out, Windows struggles to manage the page file correctly, causing problems such as full scratch discs, slowdowns, and potential errors.
It is preferable to use an SSD for virtual memory, as an HDD—which uses rotating magnetic platters and mechanical heads to read and write data—can be up to thirty times slower.
Take care not to set excessive values: sizes of 30–40 GB can cause wasted space, degraded performance, and greater fragmentation on HDDs.
To get the best performance, it is useful to enable the High Performance profile by going to Control Panel → Power Options → High Performance.
Finally, it is very important to close programmes that you are not actively using, such as Chrome, Spotify, Discord, WhatsApp Desktop, or Teams. Many of these continue to use RAM even when minimised or running in the background, which can increase the risk of virtual memory crashes or slowdowns during multitasking. Each program may occupy a separate memory segment, increasing overall memory usage. RAM is a type of volatile memory, which loses its contents when the computer is powered off, making virtual memory essential for maintaining system stability during multitasking.
PCs with Limited RAM: Practical Advice
If your PC has 4 GB or 8 GB of RAM, configuring virtual memory helps, but it does not work miracles. You can improve the situation as follows:
- Limit applications that start automatically
- Use lighter browsers
- Avoid opening many programmes simultaneously
- Maintain free space on the disc
- Consider a RAM upgrade, if possible
If your computer is dated or not expandable, consider models that have 16 or 32 GB of RAM, ideal for ensuring smooth multitasking even with Windows 11.
When Is It Worth Replacing Your PC Rather Than Increasing Virtual Memory?
Optimising Windows virtual memory settings does not always suffice. If your PC is very old, even with a perfect page file configuration, you cannot overcome the physical limitations of the hardware.
In such cases, purchasing a new computer may be more sensible than making only partial upgrades.
A new device guarantees higher performance, greater reliability, and allows you to benefit from the latest technologies and features available on the market.
Opting to purchase a GEEKOM mini PC represents an excellent solution, offering numerous advantages, such as:
- Expandable memory up to 32 or 64 GB, ideal for multitasking and demanding programmes
- Fast NVMe SSDs are perfect for managing virtual memory optimally
- Modern, quiet CPUs, suitable for both work and gaming
- Compact dimensions and low power consumption, to optimise space
- Optimal cost-to-performance ratio compared to maintaining or upgrading dated systems
For those who desire a high-performing, cutting-edge machine, these mini PCs offer an immediate quality leap that lasts over time.
Conclusion
Windows virtual memory is a fundamental tool for keeping your PC stable and fast. Configuring it correctly allows you to avoid slowdowns, virtual memory crashes, and problems such as full scratch discs.
If, after all these measures, your PC continues to struggle, it may be time to consider a more efficient solution, especially if you use professional software, manage large amounts of data, or frequently multitask.
Compact and powerful mini PCs with NVMe SSDs and fast RAM are ideal for Windows 11, and for handling demanding workloads, making the most of the page file and virtual memory.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between virtual memory and RAM?
RAM is a physical component that works rapidly and manages all current activities on the computer. Windows virtual memory, on the other hand, is the disk space that holds temporary data when physical RAM is full. It is slower but essential for avoiding freezes, maintaining reliability, and allowing the execution of multiple programmes.
What should I do when the scratch discs are full?
When scratch discs are full, you need to free up space on the main disc, delete temporary files, increase the Windows page file size, place it on a fast SSD, and then restart the system. In Photoshop: check the scratch disc settings in preferences, as slowdowns often stem from heavy cache and temporary files.
Is it better to increase RAM or modify virtual memory?
Increasing RAM remains almost always the better choice, as it offers greater speed compared to virtual memory. The page file helps prevent freezes, but remains slower. On old or non-upgradeable computers, replacing the hardware may be more cost-effective.
How much RAM and virtual memory does a modern PC need?
For browsing and light activities, 8 GB of RAM is sufficient, whilst for running many applications simultaneously, at least 16 GB is required. For graphics, gaming, or video editing, 32 GB is recommended. Windows 11 virtual memory helps manage intense workload peaks, ensuring fluidity even with demanding software.
How can I optimise virtual memory for graphics and video work?
For stability and performance, you should set virtual memory on an NVMe SSD, leave at least 50 GB free, and configure the page file correctly. If possible, increase RAM and manage the cache and temporary discs of Adobe applications, which consume considerable space during processing. Windows 11 manages the page file dynamically, whilst on Windows 10, it is advisable to configure it manually to avoid slowdowns.